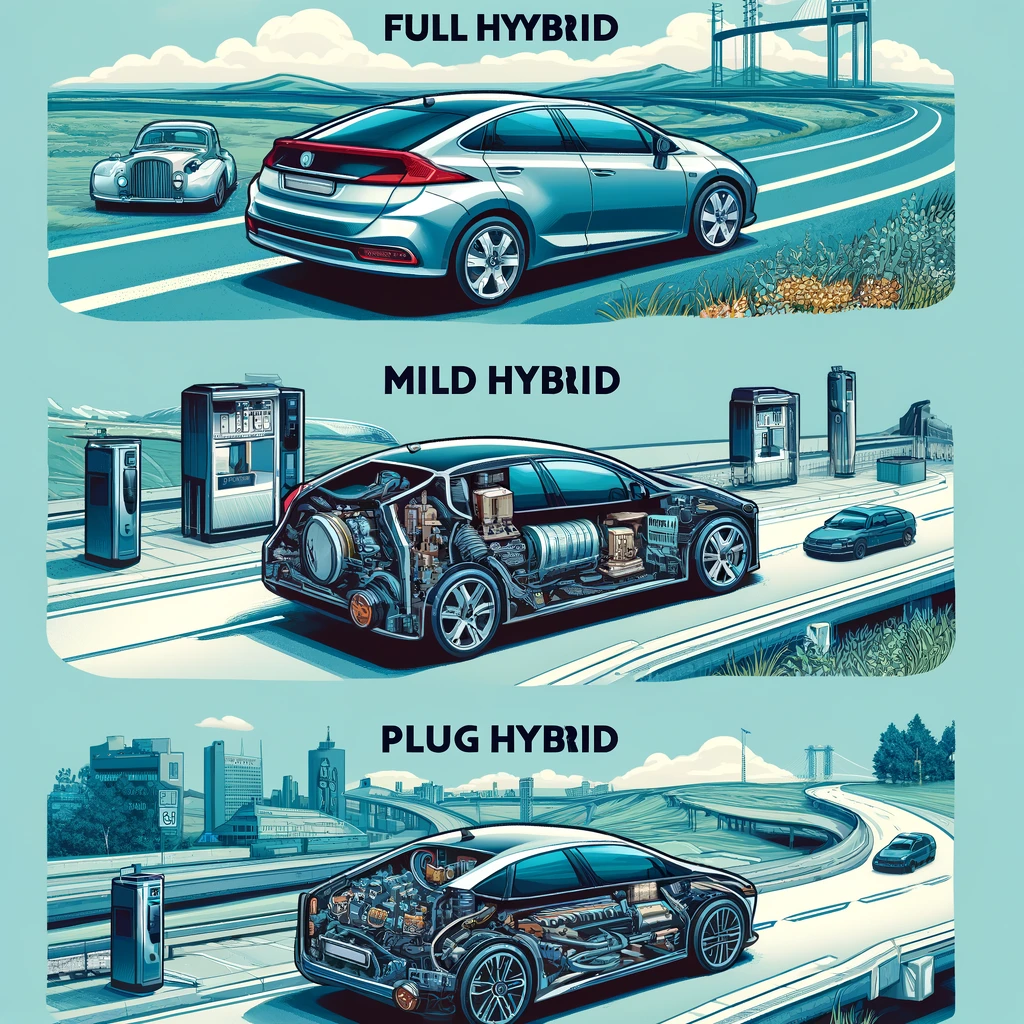
Introduction: The Growing Trend of Hybrid Vehicles
In recent years, the automotive market has seen a significant increase in the popularity of hybrid vehicles. These cars, known for their efficiency and environmental friendliness, are becoming the preferred choice for many drivers. With some hybrid models, there is even a wait of over a year for delivery. Hybrids offer a cost-effective alternative to traditional gasoline vehicles and are less restrictive compared to electric vehicles (EVs) due to their non-reliance on charging infrastructures.
Types of Hybrid Vehicles
Hybrid cars utilize a dual powertrain system that includes an engine and an electric motor. There are three main types of hybrid vehicles:
Full Hybrids (HEV)
- Overview: Full hybrids can operate by using either the engine, the electric motor, or both. This flexibility allows for optimal fuel efficiency.
- Types: There are three configurations:
- Series Hybrids: The gasoline engine generates power for the electric motor, not directly for the wheels.
- Parallel Hybrids: Both the engine and the electric motor can drive the wheels directly.
- Series-Parallel Hybrids: This type combines aspects of both series and parallel hybrids, providing more efficiency and power.
- Examples: Toyota was the pioneer in mass-producing series-parallel hybrid vehicles with models like the Prius, Camry, and various Lexus vehicles.
Mild Hybrids (MHEV)
- Overview: Mild hybrids offer a more limited use of electric propulsion. The electric motor is mainly used to assist the engine, rather than power the car independently.
- Efficiency: They enhance fuel efficiency by up to 15% compared to traditional vehicles.
- Cost and Accessibility: Mild hybrids are generally more affordable and easier to integrate with existing vehicle designs.
- Popularity: In the European market, where environmental regulations are stringent, mild hybrids are particularly popular. Models from BMW and Mercedes-Benz often feature this technology.
Plug-In Hybrids (PHEV)
- Overview: Plug-in hybrids allow for significant electric driving range, supported by an engine for longer trips.
- Electric Range: They can travel extensively on electric power alone before the gasoline engine is needed.
- Charging: PHEVs require external charging, offering a blend of EV and hybrid benefits.
- Market Positioning: Despite their advantages, the higher cost of PHEVs and lack of government incentives in some markets make them less prevalent.
Choosing the Right Hybrid

Selecting the right type of hybrid vehicle depends on individual needs:
- Daily Commute and Driving Habits: For those with longer commutes or frequent access to charging stations, a PHEV might be the ideal choice.
- Budget Considerations: If cost is a primary concern, mild hybrids offer improved efficiency without a significant initial investment.
- Environmental Impact: Those looking to maximize their environmental benefits might prefer full hybrids or PHEVs for their lower emissions during city driving.
Conclusion: The Future of Driving is Hybrid
As the automotive industry evolves, hybrids play a crucial role in the transition towards more sustainable driving solutions. Each type of hybrid offers distinct advantages, making them suited to different driving styles and needs. With ongoing advancements in technology and increasing environmental awareness, the demand for hybrids is likely to continue growing, making them a key component of the future automotive landscape.
Genesis GV80 Coupe: A New Entrant in the Coupe-Style SUV Market
Hi, I’m [jeybee]. As a long-time resident of Seoul, I’m passionate about uncovering the authentic, everyday magic of Korea. This blog is my way of sharing my favorite spots, tips, and cultural insights with you, beyond the usual tourist traps.